AutoR
Autonomer Leichtbau-Heliostat mit Radkranzantrieb
| Beginn |
1. November 2013 |
| Finanzierung |
Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Energie (BMWi) |
Projektbeschreibung
Im Rahmen des Projektes AutoR entwickelt das Institut für Telematik
Techniken zur Funkkommunikation in Industrieanlagen mit einer hohen Zahl
an Funkknoten.
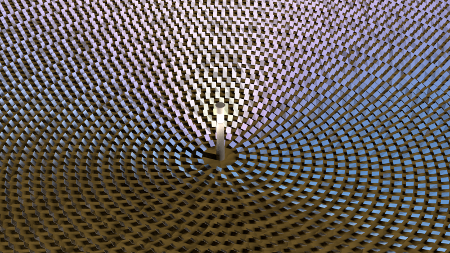
Solarturmkraftwerke sind ein wichtiger Baustein zur nachhaltigen und
zuverlässigen Energieversorgung der Zukunft. Insbesondere da sie (im
Gegensatz zur Photovoltaik) bei entsprechender Auslegung ganztägig
Energie liefern können und somit als Grundlastkraftwerke geeignet sind.
Bei einem Solarturmkraftwerk fokussieren Spiegelkonstruktionen
(Heliostate) das Sonnenlicht auf einen zentralen Absorber und die
erzeugte Wärme wird durch Wärmetauscher und Turbinen in elektrische
Energie umgewandelt.
Die Anzahl der Heliostate eines Kraftwerkes kann mehrere 10000 betragen
um einen optimalen Wirkungsgrad zu erreichen. Daher zielt das Projekt
AutoR auf die Kostenreduktion der Heliostate um die Wirtschaftlichkeit
zu erhöhen. Ein wichtiger Teilaspekt ist hierbei die Kommunikation
zwischen Heliostat und Kraftwerkssteuerung um die Heliostate der Sonne
nachzuführen und in Ausnahmesituationen (zum Beispiel bei starkem Wind)
bestimmte Positionen einzunehmen. Der klassische Ansatz mittels
drahtgebundenen Feldbussen verursacht hohe Investitionskosten für
Kabelverlegung und Blitzschutz.
Im Institut für Telematik wird hierfür einen drahtloser Feldbus
entwickelt, der die Investitionskosten auf ein Minimum reduziert und
gleichzeitig eine zuverlässige und ausfallsichere Kommunikation
gewährleistet. Dafür werden unter anderem die im Projekt HelioMesh gewonnenen Erkenntnisse auf
Zuverlässigkeit, Echtzeitfähigkeit und Skalierbarkeit auf sehr große
Netzwerke untersucht. Durch enge Verzahnung mit den anderen Projektpartnern, der Firma
Trinamic und dem DLR, wird es möglich sein die wesentlichen
Schnittstellen (zum Beispiel zwischen Mechanik und
Antennenpositionierung) anwendungsspezifisch zu optimieren und das
Komplettsystem in Feldtests zu evaluieren. Die in den Feldtests gewonnenen Erkenntnisse werden schließlich mittels
Simulation auf sehr große Netzwerke zu übertragen um die Zuverlässigkeit
bei hoher Skalierung sicherzustellen.
Publikationen
Florian Kauer,
Florian Meyer und
Volker Turau. A Holistic Solution for Reliable Over-the-Air Software Updates in Large Industrial Plants. In
Proceedings of the 13th Workshop on Intelligent Solutions in Embedded Systems (WISES 2017), Juni 2017, pp. 29–34. Hamburg, Germany.
@InProceedings{Telematik_WISES_2017,
author = {Florian Kauer and Florian Meyer and Volker Turau},
title = {A Holistic Solution for Reliable Over-the-Air Software Updates in Large Industrial Plants},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 13th Workshop on Intelligent Solutions in Embedded Systems (WISES 2017)},
pages = {29-34},
day = {12-13},
month = jun,
year = 2017,
location = {Hamburg, Germany},
}
Abstract:
In cyber-physical systems, such as modern industrial plants, complex software is an essential part that enables cost-effective and flexible operation. However, this complexity increases the probability of problems that only reveal themselves after the deployment. This is even more important if security aspects are involved. Therefore, providing the possibility for software updates is an important building block in the design of industrial plants. This paper presents a holistic concept for software updates in an industrial plant with thousands of wirelessly connected embedded devices. Using wireless technology imposes additional difficulties in terms of data rate, packet size and reliability that have to be addressed in particular. The contribution also includes an analytical model to estimate the time until a new firmware is distributed. Evaluations carried out on hardware as well as in the OMNeT++ simulator demonstrate the applicability and scalability of the proposed approach.
Florian Kauer,
Maximilian Köstler,
Tobias Lübkert und
Volker Turau. OpenDSME - A Portable Framework for Reliable Wireless Sensor and Actuator Networks (Demonstration). In
Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Networked Systems (NetSys 2017), März 2017, pp. 1–2. Göttingen, Germany.
@InProceedings{Telematik_Netsys_2017,
author = {Florian Kauer and Maximilian K{\"o}stler and Tobias L{\"u}bkert and Volker Turau},
title = {OpenDSME - A Portable Framework for Reliable Wireless Sensor and Actuator Networks (Demonstration)},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Networked Systems (NetSys 2017)},
pages = {1-2},
day = {13-16},
month = mar,
year = 2017,
location = {G{\"o}ttingen, Germany},
}
Abstract:
The Deterministic and Synchronous Multi-Channel Extension (DSME) of the IEEE 802.15.4 standard provides a data link layer for time division multiple access in wireless mesh networks. The authors present openDSME, a portable implementation for hardware and simulators which promises reliable message transfer suitable for applications in demanding industrial environments. A demonstration has been developed to illustrate the performance of openDSME in a simulated network and to show its benefits over CSMA/CA.
Florian Kauer,
Maximilian Köstler,
Tobias Lübkert und
Volker Turau. Formal Analysis and Verification of the IEEE 802.15.4 DSME Slot Allocation. In
Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems, November 2016, pp. 140–147. Malta.
@InProceedings{Telematik_MSWIM_Formal_DSME,
author = {Florian Kauer and Maximilian K{\"o}stler and Tobias L{\"u}bkert and Volker Turau},
title = {Formal Analysis and Verification of the IEEE 802.15.4 DSME Slot Allocation},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Modeling, Analysis and Simulation of Wireless and Mobile Systems},
pages = {140-147},
month = nov,
year = 2016,
location = {Malta},
}
Abstract:
Providing dependability is still a major issue for wireless mesh networks, which restrains their application in industrial contexts. The widespread CSMA/CA medium access can provide high throughput and low latency, but can not prevent packet loss due to collisions, especially in very large and dense networks. Time slotted medium access techniques together with a distributed slot management, as proposed by the Distributed Synchronous Multi-channel Extension (DSME) of the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, are promising to provide low packet loss, high scalability and bounded end-to-end delays. However, our implementation, openDSME, exposed some weaknesses. While the allocated slots allow for reliable data transmission, the slot management itself is conducted via CSMA/CA and is thus vulnerable to packet loss, eventually leading to an inconsistent slot allocation. This paper uses the UPPAAL framework for formal analysis and verification of the slot management process. The analysis identifies weaknesses of the slot allocation process under communication and node failures. However, it is shown that inconsistencies are eventually resolved and improvements to the procedure are proposed that reduce the negative impact of failed slot allocation procedures significantly.
Florian Meier und
Volker Turau. An Analytical Model for Fast and Verifiable Assessment of Large Scale Wireless Mesh Networks. In
Proceedings of the Design of Reliable Communication Networks (DRCN), März 2015, pp. 185–190. Kansas City, MO, USA.
@InProceedings{Telematik_DRCN_Model,
author = {Florian Meier and Volker Turau},
title = {An Analytical Model for Fast and Verifiable Assessment of Large Scale Wireless Mesh Networks},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Design of Reliable Communication Networks (DRCN)},
pages = {185-190},
month = mar,
year = 2015,
location = {Kansas City, MO, USA},
}
Abstract:
Ensuring reliability is a key requirement for using wireless mesh networks in industrial applications. Analytical models provide a valuable support in the design of reliable networks, especially for large scale applications, where simulations do not provide the required scalability. This paper proposes an analytical model for multi-hop IEEE 802.15.4 networks that incorporates significant improvements compared to previous models. Comparisons of the model with simulations using the MiXiM framework for OMNeT++ exhibit a very good compliance. The analytical model is therefore adequate for assessment of very large wireless mesh networks. Additionally, the model yields new insights into the characteristics of IEEE 802.15.4 networks, regarding the impact of acknowledgment collisions and the influence of hidden nodes on retransmissions.
Florian Meier und
Volker Turau.
Analytical Model for IEEE 802.15.4 Multi-Hop Networks with Improved Handling of Acknowledgements and Retransmissions. Technical Report Report arXiv:1501.07594, arXiv.org e-Print Archive - Computing Research Repository (CoRR), Cornell University, Januar 2015.
@TechReport{Telematik_ARXIV_Multihop_Networks,
author = {Florian Meier and Volker Turau},
title = {Analytical Model for IEEE 802.15.4 Multi-Hop Networks with Improved Handling of Acknowledgements and Retransmissions},
number = {Report arXiv:1501.07594},
institution = {arXiv.org e-Print Archive - Computing Research Repository (CoRR)},
address = {Cornell University},
month = jan,
year = 2015,
}
Abstract:
The IEEE 802.15.4 standard allows for the deployment of cost-effective and energy-efficient multi-hop networks. This document features an in-depth presentation of an analytical model for assessing the performance of such networks. It considers a generic, static topology with Poisson distributed data-collection as well as data-dissemination traffic. The unslotted CSMA/CA MAC layer of IEEE 802.15.4 is closely modeled as well as an enhanced model of the neighborhood allows for consideration of collisions of packets including interferences with acknowledgements. The hidden node problem is taken into account as well as a formerly disregarded effect of repeated collisions of retransmissions. The model has been shown to be suitable to estimate the capacity of large-scale multi-hop networks.
Andreas Pfahl, Michael Randt,
Florian Meier, Martin Zaschke, C.P.W. Geurts und Michael Buselmeier. A Holistic Approach for Low Cost Heliostat Fields. In
Proceedings of the SolarPACES 2014, September 2014. Beijing, China.
@InProceedings{Telematik_SolarPACES_HolisticHeliostatFields,
author = {Andreas Pfahl and Michael Randt and Florian Meier and Martin Zaschke and C.P.W. Geurts and Michael Buselmeier},
title = {A Holistic Approach for Low Cost Heliostat Fields},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the SolarPACES 2014},
month = sep,
year = 2014,
location = {Beijing, China},
}
Abstract:
The AutoR-project takes a holistic approach to reduce the cost of heliostat fields: Wireless control and energy supply enables to use smaller heliostats which need less steel per mirror area (but usually have high wiring cost). A low cost but high efficient drive system is chosen which reduces energy consumption to a minimum amount and leads to low cost for PV cell and energy storage. The usual boundary layer wind tunnels tests for heliostats are proven regarding energy spectra to avoid oversizing of steel structure and drives or failures because of underestimations of the loads. The concepts for wireless control and energy supply, the wind tunnel investigations and the first rim drive heliostat prototype are presented.
Shrirang Abhyankar, Jed Brown, Matthew Knepley,
Florian Meier und Barry Smith. Poster Abstract: Abstractions for Expressing Network Problems in PETSc. In
SIAM Workshop on Network Science, Juli 2014. Chicago, US.
@InProceedings{SIAM_PETSc,
author = {Shrirang Abhyankar and Jed Brown and Matthew Knepley and Florian Meier and Barry Smith},
title = {Poster Abstract: Abstractions for Expressing Network Problems in PETSc},
booktitle = {SIAM Workshop on Network Science},
month = jul,
year = 2014,
location = {Chicago, US},
}
Abstract:
Developing scalable software for large-scale applications, particularly for networks and circuits, is challenging due to the underlying unstructured and irregular geometry of the problem. We present a programming framework recently added to the PETSc library to easily express network problems, and thereby reduce the application development time. A brief overview of the framework is presented and two application examples, one from power grid and the other from radio networks, are discussed.
Studentische Arbeiten
Abgeschlossene Arbeiten